What You Need to Know About California Prop 65 And How We Can Help!
- Prop 65 is a proposition that requires all businesses to provide a clear and reasonable warning before exposing individuals in California to any chemical listed by the state for its potential to cause cancer or reproduce toxicity.
- The warning must name at least one of the chemicals for which the warning is being provided
- Specify the chemicals which is known to cause cancer or reproductive harm
- Include a triangular symbol (available for download here) to the left of the warning and the word “WARNING” in all capital letters and bold type
- New regulations go into effect August 30, 2018
- If a business is found to be in violation of Proposition 65, a court may order the business to stop committing the violation. The business is also subject to civil penalties of up to $2,500 per day for each violation.
Compliance with Prop 65 can be challenging given the complexity of the new requirements, but the best way to manage your company’s Prop 65 liability is to minimize the risk of being sued in the first place.

How Barcodes, Inc. Can Help:
We have the printers, labels and the label software that you need to either print your own Prop 65 warning labels or purchase pre-printed labels and allow us to do the work for you. Click on any of the images to lead you to the products that can help you get in compliance with Prop 65.
Epson TM-C3500                DP-1                  Consumables         BarTender Label Software
12Color Printer
Feel free to email Alyce Miller at [email protected] or call 312-765-8855, if you have any questions or need a quote with any of the above.
Choosing a Scanner for UPC Barcode Reading
 UPC barcodes are one of the most commons codes that are being read daily around the world. If you’re not familiar with the UPC code you can find it on any commercial product from the grocery store to the everything on Amazon.
UPC barcodes are one of the most commons codes that are being read daily around the world. If you’re not familiar with the UPC code you can find it on any commercial product from the grocery store to the everything on Amazon.
The UPC number itself is referred to as the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number). The GTIN is made up of two parts: The UPC Company Prefix and the number that you have assigned to that unique product. This information is how any business can recognize what each product is.
The UPC code is a standard 1D linear barcode so almost any device will be a suitable UPC barcode scanner. The primary concern when choosin g a scanner will be reading performance to keep up with your specific application.
Laser Scanners
By far the most common, laser scanners are more than capable of reading any UPC. These scanners often are the most cost effective solution but you will need to properly line up the red laser line with the UPC to get a good read. This usually isn’t a deal breaker but for higher volume applications you may want to look at other options. One of the most popular laser scanners today is the AirTrack S1.
Imagers
Imager-based scanners utilize a specialized camera to read a barcode as opposed to reflecting light like on a laser. This means you can capture barcodes without really aiming. Just get within the reading area of the imager and you can get a positive read. Upside down, sideways, it doesn’t matter. Imagers like the AirTrack S2Â will improve scanning accuracy and speed for faster check-out lines and inventory check-ins.
Selecting a WebScan Verifier Calibration Card
 Accurate barcode verification is key to avoiding issues with large customers like Walmart and the DoD as well as the costly fines involved with non-compliance. In addition to having the right verifier, regular calibration of your verifier is essential to consistent performance.
Accurate barcode verification is key to avoiding issues with large customers like Walmart and the DoD as well as the costly fines involved with non-compliance. In addition to having the right verifier, regular calibration of your verifier is essential to consistent performance.
All of the verifiers from Webscan are easily maintained with their various calibration cards but for many people the cards are somewhat of a mystery. In the following some of the key questions that come up with verifier calibration are covered to get you started on your way.
Why do I need to calibrate?
Calibration is the process of the adjusting Reflectance levels. Checking these levels routinely will ensure that you’re getting the most accurate results.
Do I need to calibrate more than once?
Every company has their own policy on how often you should calibrate, at Webscan we recommend you do it every 30 days.
Full Color Label Printing with Epson’s ColorWorks TM-C3500
Historically, color label printing has been either too cost prohibitive to do oneself or the quality was lacking to make it worth doing. With the Epson ColorWorks TM-C3500 both of these challenges are resolved.
With the ColorWorks C3500, you can easily customise and print your own colour labels. Whether it’s printing packaging labels with colourful logos and pictures or tickets and ID cards with important barcodes and product information, this printer ensures you can print it all from one machine. It also helps you conform with GHS international chemical labelling guidelines, as labels can be printed on-demand without using pre-printed templates.
Honeywell ESD
 You often hear manufacturers reference ESD when discussing scanners. In fact, on the Honeywell Granit datasheet you’ll see under the “Environmental†section on the back: ESD. ±20Kv air discharge, ±8KV contact discharge
You often hear manufacturers reference ESD when discussing scanners. In fact, on the Honeywell Granit datasheet you’ll see under the “Environmental†section on the back: ESD. ±20Kv air discharge, ±8KV contact discharge
What does it mean and why is it important?
- ESD – electrostatic discharge – is the sudden flow of electricity between two objects resulting from two conditions:
- Air Discharge. A high electrostatic field between two objects when they are in close proximity.
- Contact Discharge. Direct contact transfer of electricity between two objects at different potentials. This is similar to the above except you are injecting the shock directly into the computer. A typical example of this would be 20KV Air Discharge into a scanner vehicle mount. The mount in turn passes an 8KV shock to the scanner.
- Kv is a kilovolt – or 1,000 Volts. And a volt is…um…a unit of measurement to define voltage. Think of voltage, using a plumbing analogy, as water pressure.
TTL and True RS-232 Serial – What’s the Difference?
 The differences between a TTL RS232 and a True RS232 interface purely have to do with data being sent, not with powering the barcode scanner. The data is being sent as an electrical block-signal representing a sequence of logical zero’s and ones.
The differences between a TTL RS232 and a True RS232 interface purely have to do with data being sent, not with powering the barcode scanner. The data is being sent as an electrical block-signal representing a sequence of logical zero’s and ones.
- For a TTL device a zero would ideally be 0 volt, and a 1 one would ideally be 5 volt. The receiving device therefore has to decide whether a the signal at a given time is meant to be 0 or 5 volt, in order to tell if it is looking at a binary zero or a binary one.
- For a True RS232 device the zero is represented by ideally -12Volt and a one is represented by ideally + 12 Volt. Here the receiving device has it a bit easier because the difference between -12 and + 12 = 24 Volt. (specification allows -5 to -15V and +5 to +15V)
In practice we see that a signal gets weaker the longer it has to travel and can sometimes drop 1 volt a meter going via cable from device to host. With a True RS232 device both positive and negative signal can drop 10 volts and still have 4 volts difference in polarity left to tell zero’s from ones. The TTL interface has already less polarity difference if the signal drops just 2 volts.
Asset vs Inventory Tracking Explained
When explaining data tracking, the first question our customers ask is “Aren’t asset tracking and inventory tracking the same thing?†The short answer is no.
Assets are “permanent†objects that belong to a company. They are items a business uses internally, such as computers, tools or educational material. An asset is always tracked as a unique item. For example, even though you may give 10 of the exact same PC, you are managing each PC as an individual item with its own unique barcode label. You want to ensure that you have accurate information on each specific asset’s location, condition, purchase date, value, custodian and most recent maintenance.
Inventory tracking refers to objects that are sold, distributed or otherwise consumed by a company. These “temporary†objects include retail items and office supplies. For example, you may have 100 boxes of staples in inventory and when you use one box the tracked quantity decreases by one. You are not concerned with what specific box was used, but rather that 1 of 100 was removed. Ultimately, you want to know how many you have in stock and when to order more.
To begin, compare your objects with the chart below to determine if you need inventory or asset tracking:
| Description | Asset | Inventory |
|---|---|---|
| Objects used internally, such as computers, tools, and educational materials | • | |
| Track depreciation of company property | • | |
| Track maintenance on company equipment | • | |
| Objects are for sale or resale | • | |
| Ability to track/monitor reorder levels | • | |
| Objects are “temporary” and/or often replace, such a paper, pens and other consumables | • | |
| Employees may check objects in and out | • | • |
For more assistance finding the right data collection solution for your needs, contact us at Barcodes, Inc.
RFID vs Barcodes
 With the introduction of NFC, RFID has become a trendy technology, but is it really a necessity for your business? Let’s go over some of the differences between barcodes and RFID:
With the introduction of NFC, RFID has become a trendy technology, but is it really a necessity for your business? Let’s go over some of the differences between barcodes and RFID:
- Line of Sight – Rather than using light to collect or read a number from a barcode, radio waves are used to read a number from the RFID tag. Therefore, RFID does not require a line of sight to operate, but rather you can wave the RFID reader to read the tags.
- Multiple Item Scanning – Since RFID does not require line of sight it is not necessary to present each tag to the reader separately (as is required for barcodes); instead, all tags within the range of the reader can be read almost simultaneously as they pass the reader.
- Automation & Accuracy – Barcodes require a person to manually read each individual barcode, which can lead to manual read errors and mis-scanning. RFID, on the other hand, is a fully automated solution with a higher accuracy rate.
Although there is a huge savings in RFID technology from a resource, time and accuracy standpoint, we rarely recommend a business migrating from a completely manual process to a RFID solution. Companies that currently incorporate barcodes face the best return on investment from a RFID solution. Talk to one of our experts today to get a full assessment of your business.
Barcode Warehouse Management Software
Barcode warehouse management software is used to control the movement and storage of products or goods within a warehouse and process the associated transactions including, but not limited to, shipping, receiving, put away and picking through the use of barcode automatic identification and data capture (AIDC) technology.
Warehouse management systems manage the following core functions:
- Receiving – The ability to properly handle a shipment when it arrives. This process can be individualized to each warehouse or product type. In some cases, goods are not received into a facility, but rather cross-docked, which is a logistics procedure where products from a supplier or manufacturing plant are distributed directly to a customer or retail chain with marginal to no handling or storage time. Cross docking takes place in a distribution docking terminal; usually consisting of trucks and dock doors on two (inbound and outbound) sides with minimal storage space. The name ‘cross docking’ explains the process of receiving products through an inbound dock and then transferring them across the dock to the outbound transportation dock.
- Put Away – Put-away is normally thought of as the process of moving received inventory from the dock, kitting area, or production department to a storage bin. The put-away process is also used to relocate inventory within the warehouse and to replenish dedicated storage bins with inventory from a reserve storage bin. Any time inventory is being placed in a storage bin it is being put away. System directed put-away is when the WMS chooses the destination storage bin rather than the operator.
- Inventory – Inventory Technology refers to the supervision of supply, storage and accessibility of items in order to ensure an adequate supply without excessive oversupply. It also helps companies keep lost sales to a minimum by having enough stock on hand to meet demand. The inventory can be real-time or in the form of a cycle count, which is an audit procedure designed to verify the inventory accuracy for a small subset of inventory in a specific location on a specific day, thus providing an ongoing measure of inventory accuracy.
- Picking – Picking consists of taking and collecting articles in a specified quantity before shipment to satisfy a customer’s order. The following are different types of picking:
- Piece Picking (or Pick to Part) – Order pickets move to collect the products necessary for one order.
- Zone Picking – Each order picker is assigned to one specific zone and will only realize order picking within this zone.
- Wave Picking – Order picker moves to collect the products necessary for several orders.
- Sorting Systems Method – No movement of the order picker, as the products are brought to picker by an automatic system.
- Pick to Box Method – No movement of the order picker, as the picking area is organized so that there are a number of picking stations connected by a conveyor. The order picker fills the box with the products from his station and the box moves to the other picking stations until he customer order is complete.
- Packing – Packing occurs after the picking process and entails prepping a product or good for shipment by re-packaging, affixing with a shipping label, including an invoice and staging in preparation for shipment. Additionally, for certain goods or customers, there may be the requirement for kit building.
- Shipping – Shipping entails the delivery of the right product or good to the right customer or location using the right method of shipment, all while minimizing the cost. If a customer is doing their own delivery, incorporating proof of delivery allows for more accurate information and quicker confirmation to the customer. Furthermore, our software has the ability to integrate shipment tracking for customers.
Continue reading »
Understanding Epson Endorsement, Slip, and Validation Printing
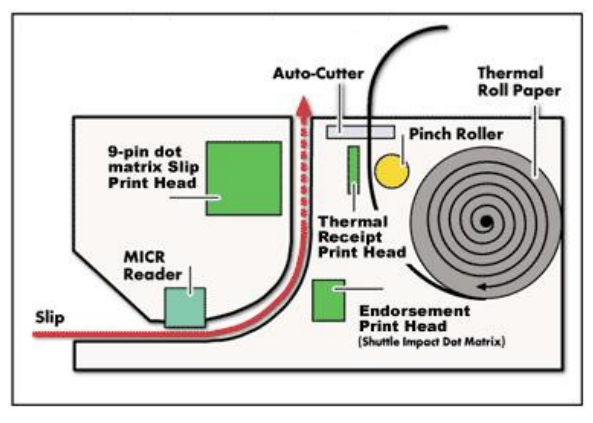 As a long standing POS printer manufacturer, Epson has provided some of the most capable and flexible printers in the market. The most common need at the POS for printing is usually a basic customer receipt, but handling things like checks, deposit slips, prescriptions, and returns will require a multi-functional printer like the TM-H600iv. These types of printers have multiple means to print on externally feed documents making them the perfect all-in-one solution for financial institutions, pharmacies, and general retail applications.
As a long standing POS printer manufacturer, Epson has provided some of the most capable and flexible printers in the market. The most common need at the POS for printing is usually a basic customer receipt, but handling things like checks, deposit slips, prescriptions, and returns will require a multi-functional printer like the TM-H600iv. These types of printers have multiple means to print on externally feed documents making them the perfect all-in-one solution for financial institutions, pharmacies, and general retail applications.
Understanding the differences between the 3 types of printing (Endorsement, Slip, and Validation) can be confusing at first but we’ve broken it down in these simple definitions and included diagram.