Barcoding Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
See our help section for information about BarcodesInc ordering and policies.
General Barcoding
How does a barcode work?
Is the price of my item in the barcode?
What is a 1D (linear) barcode? What is a 2D barcode?
How many characters can fit into a barcode?
What is the barcode on a driver’s license?
How small can I make a barcode?
UPC Number and UPC Barcode
Do I need a UPC number?
| Usage | UPC needed? |
|---|---|
| Tracking internal inventory | No |
| Selling products directly to customers | No |
| Selling products through a distributor or retailer | Most of the time (Contact your distributor or retailer to be sure) |
| Selling products through a major national store | Always |
How do I get a UPC number?
Follow this link for all the information you need to start this process: Apply for a UPC Barcode
How much does a UPC number cost?
Because the prices vary so greatly, only GS1 can give you an accurate cost for this.
What is a UPC barcode?
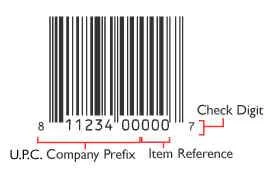
This first component, the UPC Company Prefix, is between 6 and 10 digits long, and is assigned to you by GS1. The number of digits is determined by how many products you will need to assign numbers to. So if you have thousands of products, your company prefix will need to be fewer digits. If you have just a few products, your company prefix will likely be closer to 10 digits long. This company prefix number will represent you as the manufacturer on all of your products, as well as in any EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) applications.
The second component is your unique number used to reference a specific product. It is called an “Item Reference Number.” This number is not assigned by GS1- it is up to the manufacturer to assign the unique Item Reference Number for a given product.
The last number is a check digit calculated from the previous 11 digits. It is not randomly assigned. The barcode label printing software you use to create your labels will calculate this check digit for you. You can contact BarcodesInc for help with selecting a label printing software to meet your business needs.
Can I print my own UPC barcodes?
What is the difference between direct thermal (DT) and thermal transfer (TT)?
What does ‘DPI’ mean?
How many labels are on a roll?
How do I make a barcode label?
What is a ‘dispenser’?
What is the difference between ‘desktop’ and ‘tabletop’ printers?
How does a barcode scanner work?
Do I need any special software to use a scanner?
How far is the range of a cordless barcode scanner?
Can I read a barcode off of a screen?
Is a laser scanner dangerous?
How long is the cable on a scanner?
Can my scanner read a 2D barcode?
Does a mobile computer come with software?
What does 802.11a/b/g/n mean?
How is Windows Mobile/WindowsCE different from Windows 7/Vista?
What does WAN mean? How are GSM/HSPA and EVDO different?
What does ‘batch’ mean?
Can I get online with a mobile computer?
What factors should I consider when buying an ID Card Printer?
- Volume: How many cards do you plan on printing?
- Printing Capability: Do you want to print on one side or two sides of the card?
- Printing Technology: Can your card have an unprinted border around the card or do you need “over the edge” coverage?
- Security: Do you need lamination for security and durability?
- Encoding: What technology do you plan on using with the ID card Magnetic stripe, SmartCard, or UHF RFID?
Does my choice of printer differ based on card volumes?
Printers are grouped into 3 categories:
- Value – The most economical of the ID Card printers. With a limited footprint and scaled down capabilities, this printer is perfect for small printing jobs and jobs on-the-go. Printers in the category are perfect for print volumes under 1,000 prints.
- Standard – A step up in design and printing capabilities, this class of printer offers a reliable print output with a moderate footprint. Printers in the category typically can handle 1,000 – 10,000 prints and are perfect for small and medium businesses.
- Premium – The most robust printers in the industry. These printers tend to occupy a larger footprint and typically offer more options for lamination and printing technologies. Printers in the category typically can handle a volume of 10,000 – 25,000 prints and it designed for high volume and high security requirements.
Do I need a single or dual side printer?
What is the difference between Direct-to-card and Reverse transfer?
Reverse Transfer is less common than Direct to Card and transfers an image to a retransfer film. This film is applied to the blank card which provides “over the edge” coverage and vibrant, durable print.
Do I need lamination for my ID Cards?
- Security : Lamination provides an extra layer of security for your ID card, by reducing the possibility of counterfeit cards and eliminating any tampering with the information contained in the card
- Durability : Lamination provides extra durability for standard ID Cards. Purchasing a printer with a laminating option is ideal for cards in harsh conditions/environments and situations where continual use provides excessive wear and tear on the cards.
- Cost savings : Although printers with laminating capabilities can be a larger upfront cost, they yield significant cost savings down the road due to the elimination of security incidents and reduction of card printing supplies
What encoding options do I have for my card?
- Magnetic Stripe : This type of card is capable of storing data on a band of magnetic material. The magnetic stripe (also known as swipe card or magstripe) is read by physical contact when swiped past a magnetic reading head.
- Contact Smart Card : A contact area of approximately .15 sq in. comprised of several gold-plated contact pads are embedded onto the card. These provide electrical connectivity when touched to or inserted into a reader
- Contactless Smart Card : These contain a re-writeable smart card microchip that can process and store data. They communicate with a terminal via radio waves with a read range of up to around 5 in.
- Gen 2 UHF RFID : RFID cards store data that can be read through radio waves at wider read ranges (typically 3 to 10 ft.), allow multiple card reads at the same time and are extremely secure.